ETF Dictionary
What is PE Ratio?
Understanding about PE Ratio- A Beginner’s Guide to Investing in ETFs.
This guide will explain the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio, and how it helps investors, especially when considering Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs).
1. What is P/E Ratio?
- P/E Ratio or Price-to-Earnings ratio, is a fundamental metric used to evaluate whether a company’s stock is worth buying. The PE ratio is the price of a share divided by its earnings. It compares the current price of a stock to how much profit it’s making per share.
- To calculate the P/E ratio, divide the stock’s current price by its earnings per share (EPS). The formula of the P/E ratio = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share
|
|
- Example: on 05/12/2022, stock AAM is priced at 30,000 VND, and its EPS was at 2,500 VND. So, The P/E ratio =30,000 VND/ 2,500 VND = 12. This means investors are willing to pay 12 VND for each unit of profit from the company’s stock.
2. PE Ratio of Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF)
- ETFs are like baskets filled with different stocks or assets, these funds typically track a benchmark index and are traded on the stock market. Similar to individual stocks, ETFs also have P/E ratios, calculated based on the collective P/E ratios of the assets within the ETF’s portfolio.
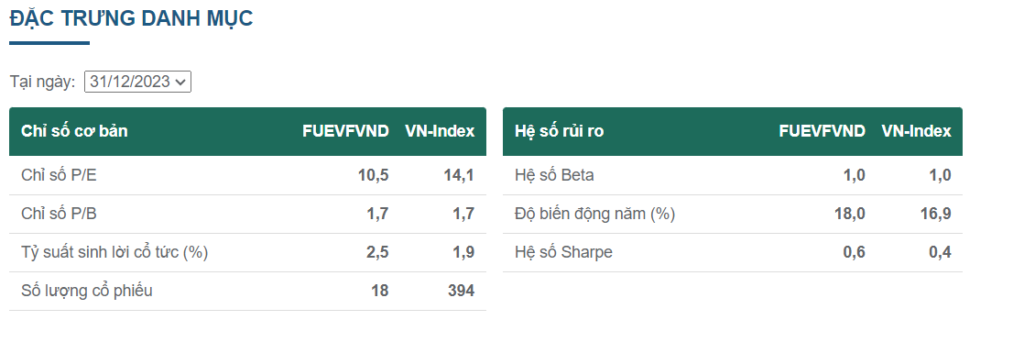
- For example, the DCVFMVN DIAMOND ETF (FUEVFVND), tracks high-performing companies in Vietnam. If this ETF has a P/E ratio of 10.5, investors are paying 10.5 VND for every 1 VND of profit generated by the companies held within the ETF.
|
|
- The PE ratio of FUEVFVND is 10.5, while the total VN-Index is 14.1, This may show that investors are paying less for each unit of profit generated by the FUEVFVND ETF compared to the entire market, the FUEVFVND ETF contains stocks that demonstrate relatively stronger earnings performance compared to the broader market.
3. Using PE Ratio to Choose Exchange-Traded Fund (ETFs)
When choosing ETFs, the P/E ratio can be a useful tool in the decision-making process.
| 1. High |
|
|
| 2. Low |
|
|
| 3. Negative |
|
- Another example of two funds: ETF A and ETF B; ETF A has a P/E ratio of 18 while ETF B has a ratio of 15. Despite ETF A having a higher P/E ratio, indicating it may seem more expensive, further analysis shows that ETF B contains fast-growing top-ranked companies, while ETF A holds mature, established companies with slower growth prospects. This highlights the importance of considering factors like the F/B Ratio, the company’s financial health and growth prospects beyond the P/E ratio when making investment decisions.
- The information provides a basic understanding of the P/E and its significance in choosing stocks or ETFs. For newbies, investing in ETFs might be a safer option as it doesn’t require in-depth knowledge of individual stocks. Hope that helps!
>> Learn more: What is PB?
Follow KIS Vietnam to update the latest Vietnam Fund and investment knowledge.
- Website: https://prime.kisvn.vn/
- Vietnam Exchange Traded Fund: KIS Prime
- Knowledge A-Z: Education
=> Follow KIS Vietnam to update the latest Vietnam Fund and investment knowledge.
- Website: https://prime.kisvn.vn/
- Vietnam Exchange Traded Fund: KIS Prime
- Knowledge A-Z: Education